 Free shipping on orders over $250 Use code SHIP4FREE
Free shipping on orders over $250 Use code SHIP4FREE
Fast Lead Times | Fast Shipping
- Pre-Terminated Fiber Optic Assemblies
- back
- In Stock Pre-Terminated
- Indoor Plenum
- Indoor / Outdoor
- Indoor Plenum Interlock Armor
- Indoor Ultra Thin Armored
- I/O Plenum Interlock Armor
- Indoor / Outdoor Ultra Thin Armored
- Outdoor SST Drop Self Supporting
- Outdoor Loose Tube (OSP)
- Outdoor Gel Filled (OSP)
- Outdoor Ultra Thin Armored (OSP)
- Outdoor Armored Direct Burial (OSP)
- Outdoor Aerial with Messenger (OSP)
- Tactical and Rugged Deployable
- back
- Multimode OM3 Tactical
- Multimode OM4 Tactical
- Singlemode Tactical
- OpticalCON Tactical
- back
- 2 Fiber OM3 - Broadcast Tactical
- 2 Fiber SM - Broadcast Tactical
- 4 Fiber OM3 - Broadcast Tactical
- 4 Fiber SM - Broadcast Tactical
- 12 Fiber OM3 - Broadcast Tactical
- 12 Fiber SM - Broadcast Tactical
- DUO Chassis Connector
- Neutrik D-Series Patch Panel
- DUO SM Inline Coupler
- DUO OM3 Inline Coupler
- DUO APC Inline Coupler
- OpticalCON MTP 12 Chassis Connector
- 2 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- 1 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- HMA Expanded Beam Tactical
- back
- 2 Channel/Fiber
- 4 Channel/Fiber
- Ex. Beam 2 CH/F MM OM3 Chassis Conn.
- Ex. Beam 4 CH/F MM OM3 Chassis Conn.
- 4 CH to 2 X 2 CH OM3 Ex. Beam
- 2 CH OM3 Ex. Beam to OpticalCON Duo
- 4 CH OM3 Ex. Beam to OpticalCON Quad
- 4 CH OM3 Ex. Beam to 2 x OpticalCON Duo
- Ex. Beam Color Coding Ring
- 1 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- 2 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- Ex. Beam 1 CH/F MM OM3 Rotary Joint
- Ex. Beam 2 CH/F MM OM3 Conn. Mod.
- Ex. Beam 4 CH/F MM OM3 Conn. Mod.
- Mil-Tac Tactical Assemblies
- Neutrik® OpticalCON®
- back
- OpticalCON DUO
- back
- 2 Fiber SM - Broadcast Tactical
- 2 Channel SM - Mil-Tac Extreme
- 2 Fiber SM Hybrid SMPTE
- 2 Fiber OM3 - Broadcast Tactical
- 2 Fiber OM3 - Mil-Tac Extreme
- 2 Fiber SM - Tactical Patch Cable
- 2 Fiber OM3 - Tactical Patch Cable
- SM Duo to 2 Simplex Breakout Assembly
- OM3 Duo to 2 Simplex Breakout Assembly
- DUO Chassis Connector
- DUO Chassis Connector
- Neutrik D-Series Patch Panel
- DUO OM3 Inline Coupler
- DUO SM Inline Coupler
- DUO APC Inline Coupler
- 1 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- OpticalCON QUAD
- back
- 4 Fiber SM - Broadcast Tactical
- 4 Fiber SM - Mil-Tac Extreme
- 4 Fiber OM3 - Broadcast Tactical
- 4 Fiber OM3 - Mil-Tac Extreme
- 4 Channel SM Lite Tac Patch
- 4 Fiber OM3 - Tac Patch Cable
- SM Quad to 4 Simplex Breakout Assembly
- OM3 Quad to 4 Simplex Breakout Assembly
- QUAD Chassis Connector
- Neutrik D-Series Patch Panel
- QUAD OM3 Inline Coupler
- QUAD SM Inline Coupler
- QUAD APC Inline Coupler
- SHUTTER BUDDY
- 1 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- 2 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- OpticalCON MTP
- back
- 12 Fiber SM - Broadcast Tactical
- 12 Fiber SM - Mil-Tac Extreme
- 12 Fiber OM3 - Broadcast Tactical
- 12 Fiber OM3 - Mil-Tac Extreme
- 12 Channel MTP SM Lite Tac Patch
- 12 Fiber OM3 - Tac Patch Cable
- SM MTP to 12 Simplex B/O Assembly
- OM3 MTP to 12 Simplex B/O Assembly
- OpticalCON MTP 12 Chassis Connector
- Neutrik D-Series Patch Panel
- OM3 Multimode Inline Coupler
- Singlemode APC Inline Coupler
- 1 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- 2 Port D-Series Wall Plate
- Hybrid Fiber + Power
- MTP Trunk Cables, Fanouts, & Cassettes
- back
- Indoor MTP Trunks
- Indoor/Outdoor MTP Trunks
- Indoor Armored MTP Trunks
- In/Outdoor Armored MTP Trunks
- Outdoor Loose Tube MTP Trunks
- Outdoor Self Sup. Drop MTP Trunks
- Outdoor Micro Armored MTP Trunks
- Outdoor Armored MTP Trunks
- IP68 Weatherproof OptiTip® HMFOC
- Stock Indoor MPO Cables
- Stock In/Outdoor MTP/MPO Trunks
- Indoor MTP Fanouts
- back
- Multimode OM3 50/125
- back
- 1 x 12 MTP to 12 Simplex Connectors
- 2 x 12 MTP to 24 Simplex Connectors
- 4 x 12 MTP to 48 Simplex Connectors
- 6 x 12 MTP to 72 Simplex Connectors
- 8 x 12 MTP to 96 Simplex Connectors
- 12 x 12 MTP to 144 Simplex Connectors
- 1 x 24 MTP to 24 Simplex Connectors
- 2 x 24 MTP to 48 Simplex Connectors
- 3 x 24 MTP to 72 Simplex Connectors
- 4 x 24 MTP to 96 Simplex Connectors
- 6 x 24 MTP to 144 Simplex Connectors
- Multimode OM4 50/125
- back
- 1 x 12 MTP to 12 Simplex Connectors
- 2 x 12 MTP to 24 Simplex Connectors
- 4 x 12 MTP to 48 Simplex Connectors
- 6 x 12 MTP to 72 Simplex Connectors
- 8 x 12 MTP to 96 Simplex Connectors
- 12 x 12 MTP to 144 Simplex Connectors
- 1 x 24 MTP to 24 Simplex Connectors
- 2 x 24 MTP to 48 Simplex Connectors
- 3 x 24 MTP to 72 Simplex Connectors
- 4 x 24 MTP to 96 Simplex Connectors
- 6 x 24 MTP to 144 Simplex Connectors
- Singlemode 9/125
- back
- 1 x 12 MTP to 12 Simplex Connectors
- 2 x 12 MTP to 24 Simplex Connectors
- 4 x 12 MTP to 48 Simplex Connectors
- 6 x 12 MTP to 72 Simplex Connectors
- 8 x 12 MTP to 96 Simplex Connectors
- 12 x 12 MTP to 144 Simplex Connectors
- 1 x 24 MTP to 24 Simplex Connectors
- 2 x 24 MTP to 48 Simplex Connectors
- 3 x 24 MTP to 72 Simplex Connectors
- 4 x 24 MTP to 96 Simplex Connectors
- 6 x 24 MTP to 144 Simplex Connectors
- 2 x 12 MTP to 24 Simplex Connectors
- 4 x 12 MTP to 48 Simplex Connectors
- Indoor / Outdoor MTP Fanouts
- MTP OSP Loose Tube Fanout Cable
- MTP OSP Armored Fanout Cable
- Stock Indoor MPO Fanout Cables
- Cassettes and Components
- back
- OM3 Cassettes
- OM4 Cassettes
- Singlemode Cassettes
- Enclosures
- back
- Super High Density 5 panel (1U)
- Super High Density 14 panel (2U)
- Lightweight Aluminum 2 panel (1U)
- Lightweight Aluminum 3 panel (1U)
- Lightweight Aluminum 4 panel (2U)
- Lightweight Aluminum 6 panel (2U)
- Lightweight Aluminum 12 panel (4U)
- Multilink 2 Panel (1U)
- Multilink 3 panel (1U)
- Multilink 4 panel (2U)
- Multilink 6 panel (2U)
- Multilink 12 panel (2U)
- 4 panel (1U) UHD Patch Panel
- Couplers and Adapter Panels
- MTP/MPO to LC LGX Cable Harness
- Fiber Patch Cables, Enclosures, & Couplers
- back
- Fiber Enclosures & Adapter Panels
- back
- Rack Mount Termination Boxes
- back
- Lightweight Aluminum 2 panel (1U)
- Multilink 2 Panel (1U)
- 2 panel (1U) Slide Out 16 AWG
- Lightweight Aluminum 3 panel (1U)
- 3 panel (1U) Swing Out Splice Box
- 3 panel (1U) LGX Patch Panel
- Multilink 3 panel (1U)
- 3 panel (1U) Slide Out 16 AWG
- 4 panel (1U) UHD Patch Panel
- Lightweight Aluminum 4 panel (2U)
- Multilink 4 panel (2U)
- Lightweight Aluminum 6 panel (2U)
- Multilink 6 panel (2U)
- Lightweight Aluminum 12 panel (4U)
- Multilink 12 panel (2U)
- Super High Density 5 panel (1U)
- Wall Mount Termination Boxes
- back
- QuickTreX 2 Adapter / 1-4 Fiber
- Lightweight Aluminum 1 panel
- Heavy Duty Steel 1 panel
- Multilink 1 Panel
- Multilink 1 Panel w/ Splice
- Lightweight Aluminum 2 panel
- Multilink 2 Panel
- Lightweight Aluminum 4 panel
- Multilink 4 Panel
- Multilink 4 Panel with Splice
- QuickTreX 2 Adapter / 1-4 Fiber
- QuickTreX 8 Adapter / 1-16 Fiber
- Outdoor Harsh Environment
- back
- QuickTreX 1 Adapter / 1-2 Fiber
- QuickTreX 2 Adapter / 1-4 Fiber
- QuickTreX 8 Adapter / 1-16 Fiber
- QuickTreX 16 Adapter w/Splice - IP65
- QuickTreX 6 Panel Steel w/Splice
- QuickTreX 24 Adapter w/Splice - IP65
- Multilink 2 Panel Outdoor
- QuickTreX 1-36F Aerial/Wall Splice/Splitter Box
- QuickTreX 144 Fiber Aerial Splice Enclosure
- QuickTreX 480 Splice Dome Enclosure
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber Splice
- 4 panel Outdoor NEMA Enclosure
- Dome Pedestal Enclosure
- Multimode OM1 Adapter Panels
- Multimode OM2/3/4 Adapter Panels
- back
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber LC
- QuickTreX 24 Fiber LC
- Multilink 12 Fiber LC
- Multilink 24 Fiber LC
- QuickTreX 6 Fiber SC
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber SC
- Multilink 6 Fiber SC
- Multilink 12 Fiber SC
- Multilink 6 Fiber ST
- Multilink 12 Fiber ST
- QuickTreX 6 Fiber ST
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber ST
- QuickTreX 6 Fiber FC
- Corning CCH to LGX Conversion Panel
- Multimode OM5 Adapter Panels
- Singlemode Adapter Panels
- back
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber LC UPC
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber LC APC
- Multilink 12 Fiber LC UPC
- Multilink 12 Fiber LC APC
- QuickTreX 24 Fiber LC UPC
- QuickTreX 24 Fiber LC APC
- Multilink 24 Fiber LC UPC
- Multilink 24 Fiber LC APC
- QuickTreX 6 Fiber SC UPC
- QuickTreX 6 SC APC
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber SC UPC
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber SC APC
- Multilink 6 Fiber SC UPC
- Multilink 6 Fiber SC APC
- Multilink 12 SC UPC
- Multilink 12 SC APC
- MTP Adapter Panels
- Blank Adapter Panels
- Splice Trays
- Custom Fiber Optic Patch Cables
- Custom Armored Fiber Patch Cables
- Stock Tactical Fiber Patch Cables
- back
- Stock Tac SM - Duplex LC UPC - 100FT
- Stock Tac SM - Duplex LC APC - 100FT
- Stock Tac SM - Duplex SC UPC - 100FT
- Stock Tac SM - Duplex SC APC - 100FT
- Stock Tac SM - Simplex LC UPC - 100FT
- Stock Tac SM - Simplex LC APC - 100FT
- Stock Tac SM - Simplex SC UPC - 100FT
- Stock Tac SM - Simplex SC APC - 100FT
- Stock Duplex Fiber Patch Cables
- Stock Uniboot Fiber Patch Cables
- Stock Simplex Fiber Patch Cables
- Fiber Optic Couplers & Attenuators
- back
- Multimode OM1 62.5/125
- back
- LC Simplex w/ Flange
- LC Duplex w/ Flange
- SC Simplex w/o Flange
- SC Simplex w/ Flange
- SC Simplex w/ Flange and Hinged Door
- LC Quad w/ Flange
- SC Duplex w/ Flange
- ST Simplex - Universal MM/SM w/o Flange
- FC Simplex - Universal MM/SM w/o Flange
- ST Simplex - Universal MM/SM w/Flange
- ST Duplex - Universal MM/SM w/Flange
- Multimode OM3/4 50/125
- back
- LC Duplex w/ Flange
- LC Quad w/o Flange
- LC Quad w/ Flange
- SC Simplex w/o Flange
- SC Simplex w/ Flange
- SC Duplex w/ Flange
- ST Simplex - Universal MM/SM w/o Flange
- FC Simplex - Universal MM/SM w/o Flange
- ST Simplex - Universal MM/SM w/Flange
- MPO Coupler - MM OM3 / OM4 Aqua
- ST Duplex - Universal MM/SM w/Flange
- Multimode OM5 50/125
- Singlemode
- back
- LC UPC Simplex w/o Flange
- LC APC Simplex w/o Flange
- LC UPC Duplex w/ Flange
- LC APC Duplex w/ Flange
- LC UPC Quad w/o Flange
- LC APC Quad w/o Flange
- SC UPC Simplex w/ Flange
- SC UPC Simplex w/o Flange
- SC UPC Simplex w/ Flange and Hinged Door
- SC APC Simplex w/ Flange
- SC APC Simplex w/o Flange
- SC APC Simplex w/ Flange and Hinged Door
- SC UPC Duplex w/ Flange
- SC APC Duplex w/ Flange
- ST Simplex - Universal MM/SM w/Flange
- ST Simplex - Universal MM/SM w/o Flange
- Keystone Couplers & Accessories
- back
- LC Duplex MM OM1 - Ivory
- LC Duplex MM OM3 / 4 - Aqua
- LC Duplex MM OM5 - Lime Green
- LC UPC Duplex SM - Blue
- LC Duplex SM APC - Green
- SC Simplex MM OM1 - Beige
- SC Simplex MM OM3 / 4 - Aqua
- SC UPC Simplex SM - Blue
- SC APC Simplex SM - Green
- MTP Singlemode
- MTP Multimode OM3/4
- Gloss Finish Keystone Wallplates
- Easy Wallplate Bracket
- 12 Port - 1U
- 6 Port LGX Blank Keystone Adapter Panel
- MTP / MPO Couplers
- Optical Attenuators
- Fiber Optic Splitters
- Mode Conditioning Fiber Cables
- Bulk Fiber Optic Cable, Testing, & Cleaning
- back
- Unterminated Fiber Optic Cable
- Fiber Optic Pigtail Kits
- back
- OM1 62.5/125 Multimode
- OM3 50/125 Multimode
- OM4 50/125 Multimode
- OM5 50/125 Multimode
- Singlemode
- back
- 1 meter LC 6 Fiber
- 3 meter LC 6 Fiber
- 3 meter SC 6 Fiber
- 1 meter ST 6 Fiber
- 3 meter ST 6 Fiber
- 1 meter LC 12 Fiber
- 3 meter LC 12 Fiber
- 3 meter LC APC
- 3 meter LC 12 Fiber Ribbon
- 3 meter SC APC 12 Fiber
- 3 meter SC 12 Fiber
- 3 meter SC UPC 12 Fiber Ribbon
- 1 meter ST 12 Fiber
- 3 meter ST 12 Fiber
- 2 meter LC 1 Fiber
- 2 meter SC 1 Fiber
- Fiber Optic Splice Trays & Boxes
- back
- Fiber Optic Splice Enclosures
- back
- Multilink 2 Panel Outdoor
- QuickTreX 8 Adapter / 1-16 Fiber
- QuickTreX 16 Adapter w/Splice - IP65
- QuickTreX 480 Splice Dome Enclosure
- QuickTreX 144 Fiber Aerial Splice Enclosure
- QuickTreX 24 Adapter w/Splice - IP65
- QuickTreX 6 Panel Steel w/Splice
- Multilink 1 Panel w/ Splice
- Multilink 4 Panel with Splice
- Lightweight Aluminum 1 panel
- 3 panel (1U) Swing Out Splice Box
- QuickTreX 12 Fiber Splice
- Fiber Optic Splice Trays
- Fiber Optic Supplies & Tools
- Fiber Optic Cleaning Products
- Fiber Optic Test Instruments
- Fusion Splicers and Accessories
- Fiber Optic Loopback Testers
- Fiber Optic Mounting Hardware
- Fiber Optic Reference Cable Kits
- Ethernet Patch Cables, Bulk Cable, & Accs.
- back
- Ethernet Patch Cables
- back
- Tactical & Rugged Deployable
- back
- Cat 5E Shielded - Custom Length
- Stock 40FT Cat 5E Shielded
- Cat 6A Shielded - Custom Length
- Stock 30FT Cat 6A Shielded
- RJ45 etherCON Coupler
- RJ45 etherCON Coupler w/ Sealing Kit
- RJ45 Cat 6A etherCON Coupler - Black
- Cat 6A etherCON Coupler - Nickel
- Neutrik D-Series Patch Panel
- Cat 6 Outdoor Inline
- Cat 6A Outdoor Panel Mount w/Cap
- Cat 6A Outdoor Panel Mount
- Cat 6 Outdoor Panel Mount
- Cat 6 Outdoor Panel Mount w/Cap
- Outdoor Patch Cable Cap
- Cat 5E Custom Made in the USA
- Cat 5E Stock
- Cat 6E Custom Made in the USA
- Cat 6 Stock
- Cat 6A Custom Made in the USA
- Cat 6A Stock
- Cat 6A Stock Outdoor Armored
- Stock Cat 6A Shielded Tactical
- Outdoor Custom Made in the USA
- Cat 6 Outdoor
- Cat 8 Custom Made in the USA
- Cat 7 Stock
- Cat 8 Stock
- 110 Cat 5 Custom Patch Cables
- Custom Cable Bundles
- Bulk Ethernet Cable
- back
- Cat 5e Unshielded
- back
- PVC, (CM), Stranded, 1000ft
- PVC, Riser (CMR), Solid, 1000 ft
- 24AWG Solid Riser , 1000 ft
- Plenum Rated Solid 1000FT USA Made
- Solid Plenum 1000FT
- 24AWG Solid Plenum, 1000 ft
- Direct Bury, CMX, Solid, 1000 ft
- 24 AWG Direct Burial Solid, 1000 ft
- 24 AWG Outdoor DB 1000FT USA Made
- Cable Reel Deployment Caddy
- Cat 5E Shielded
- Cat 6 / 6e Unshielded
- back
- PVC, (CM), Stranded, 1000ft
- PVC, 28 AWG Stranded, 1000 ft
- PVC Riser (CMR), Solid, 1000 ft
- 23AWG Solid Riser (CMR), 1000 ft
- Plenum (CMP), Solid, 1000 ft
- 23AWG Solid Plenum (CMP), 1000 ft
- Outdoor DB Solid 1000FT USA Made
- Direct Burial, CMX, Solid, 1000 ft
- Outdoor w/Messenger 1000FT USA Made
- Cable Reel Deployment Caddy
- Cat 6 / 6E Shielded Bulk Cable
- Cat 6A Unshielded
- Cat 6A Shielded
- Cat 7A Shielded
- Cat 8 Shielded
- Data & Voice Connectors
- back
- Keystone Jacks
- back
- Cat 5E - 90° Punch Down
- Cat 5E - 180°Punch Down
- Cat 6 - 90° Punch Down
- Cat 6 - 180° Punch Down
- Cat 6 Shielded 90° Punch Down
- Cat 6A - 90° Punch Down
- Cat 6A Shielded 90 Degree
- Cat 6A Shielded -180° Toolless
- Cat 8 Shielded - 90° Toolless
- Cat 8 Shielded - 90° Toolless w/Door
- RJ-11/12 Voice - 90° Punch Down
- Keystone Couplers
- Modular Plugs
- back
- Cat 5E UTP - 100 pcs USA Made
- Cat 6/6E UTP - 100 pcs USA Made
- Cat 5E/6E STP - 50 pcs USA Made
- Cat 5E/6E STP - 10 pcs USA Made
- Cat 6A STP - 50 pcs USA Made
- Cat 6A STP - 10 pcs USA Made
- Cat 8 STP - 10 pcs
- Cat 8 STP - 25 pcs
- Cat 8 STP Toolless
- Cat 6A UTP - 100 pcs
- Cat6 UTP Feed Through - 100 pcs
- Cat 6 STP Feed Through - 100 pcs
- Strain Relief Boots
- Wallplates and Surface Mount Boxes
- Splitters
- Coaxial F Connectors
- Ethernet Patch Panels
- Datacom Tools and Testers
- back
- Data & Voice Tools
- back
- PRO RJ-45 Crimper
- PRO Large OD Crimper
- Hex Crimper
- Economy RJ-45 Crimper
- PRO 110 Impact Termination Tool
- 110 Replacement Blade
- 66 Replacement Blade
- EZ RJ45 Keystone Jack Crimper
- Economy Termination Tool
- Wire and Kevlar Scissors
- Large OD Cable Stripper & Cutter
- UTP & STP Cable Stripper
- Electrical Wire Stipper
- Coaxial Cable Cutter
- Conductor Separator & Straightener
- QuickTreX Premium Adjustable Hat
- Test Equipment
- Cable Installation
- Coaxial CATV Tools
- Hand Tools
- Cable Reels
- Bulk Coaxial, Audio, and Power Cable
- back
- Co-ax RG-6 Shielded Bulk Cable
- back
- Dual Shield CCS Riser, 1000 ft WT
- Quad Shield CCS Riser, 500 ft BK
- Quad Shield CCS Riser, 1000 ft BK
- Quad Shield CCS Plenum, 1000 ft WT
- Quad Shield Solid Copper Plenum, 1000
- Dual Shield Direct Burial CCS, 1000 ft BK
- Quad Shield Direct Burial CCS, 1000 ft BK
- RG6 F Male Compression 10 Pack
- Cable Reel Deployment Caddy
- Composite Cable & Cable Bundles
- Power Cable Bulk
- Thermostat Bulk Cable
- back
- 18/2 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- 18/3 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- 18/4 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- 18/5 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- 18/6 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- 18/8 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- 20/2 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- 20/5 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- 20/8 Riser Rated, Solid Copper PVC, 500 ft
- Cable Reel Deployment Caddy
- Audio Cable Bulk
- IT Technician Tool Kits and Cases
- RJ45 Dust Plugs, Caps, and Locks
- Cable Mounting Hardware
- HDMI Cables
- Power Cords and Supplies
- Harsh Environment Cables, FTTA, RF, & IP68
- back
- OptiTip, OptiTap, HMA, & FTTA
- RF Cable Assemblies
- RF Connectors & Adapters
- back
- RF Connectors
- back
- Mini-UHF Male Crimp
- Mini-UHF Male Crimp RG-58/U
- UHF Male Solder
- UHF Male Crimp
- M Male Crimp
- N Male Crimp 50 ohm
- N Male Crimp G,G,T, 50 ohm
- N Male Crimp For Cable Group X S,G,T
- N Male Crimp RG-142/U & RG-55/U
- N Male Crimp for Cable Group B N,G,T
- SMA Male Crimp
- SMA Male Crimp RG-8/X
- SMA Male Crimp for Cable Group B N,G,T
- BNC Male Crimp RG58/U
- TNC Male Crimp RG-58/U
- TNC Male Crimp RG-8X
- RF Adapters
- Harsh Env. Fiber Optic Assemblies
- Toolkits, Cases & Enclosures
- back
- Termination Boxes
- back
- Multilink 2 Panel Outdoor
- 4 panel Outdoor NEMA Enclosure
- Dome Pedestal Enclosure
- QuickTreX 2 Adapter / 1-4 Fiber
- QuickTreX 8 Adapter / 1-16 Fiber
- QuickTreX 16 Adapter w/Splice - IP65
- QuickTreX 6 Panel Steel w/Splice
- QuickTreX 24 Adapter w/Splice - IP65
- QuickTreX 1-36F Aerial/Wall Splice/Splitter Box
- QuickTreX 144 Fiber Aerial Splice Enclosure
- QuickTreX 480 Splice Dome Enclosure
- Network IT Toolkits
- Network IT Tool Cases
- Ethernet Patch Cables & Bulk Cable
- back
- Copper Cables and Assemblies
- Bulk Outdoor Copper Cable
- Outdoor Patch Cables
- Outdoor Accessories
- back
- Cat 6 Outdoor Panel Mount
- Cat 6 Outdoor Panel Mount w/Cap
- Cat 6 Shielded Outdoor Panel Mount
- Cat 6 Shielded Outdoor Panel Mount w/Cap
- Outdoor Patch Cable Cap
- 1 Gang Outdoor Wallplate
- Water-Resistant 1 Gang
- 1 Port (1 Gang) Stainless Steel Keystone Wall Plate for Mounting RJ45 Keystone Connectors and Couplers
- Network Switches, SFPs, Converters, & Racks
- back
- Network Switches
- back
- Unmanaged Gigabit
- Managed Gigabit
- Unmanaged Gigabit PoE
- back
- QuickTreX 8 Port GIG w/ 4xRJ45,1xRJ,1xSFP
- QuickTreX 12 Port GIG w/ 8xRJ45,2xRJUL,2xSFP
- QuickTreX 24 Port GIG w/ 24xRJ45 & 2xSFP
- QuickTreX 48 Port GIG w/ 48xRJ45 & 2xSFP
- 8 Port Gigabit w/ 2 Gigabit SFP Ports
- 16 Port Gigabit w/ 2 Gigabit SFP Ports
- 24 Port Gigabit w/ 2 Gigabit SFP Ports
- 4 Port Gigabit
- Managed Gigabit PoE
- back
- QuickTreX 8 Port GIG w/ 8xRJ45 & 2xSFP
- QuickTreX 24 Port GIG w/ 24xRJ45 & 4xSFP/RJ45
- QuickTreX 36 Port 10G UL w/ 24xRJ45, 8xSFP, 4xSFP+
- 8 Port Gigabit w/ 2 Gigabit SFP Ports
- 24 Port Gigabit w/ 2 Gigabit SFP Ports
- 24 Port G w/ 4 x GIG SFP Ports + PoE Inj
- 24 Port Gigabit w/ 4 x 10Gigabit SFP Ports
- 24 Port Gigabit w/ 2 SFP Ports (Full Power)
- 24 Port Gigabit w/ 4 SFP+ Ports (Full Power)
- Unmanaged Industrial Switches
- Managed Industrial Switches
- Unmanaged Industrial PoE Switches
- back
- QuickTreX 6 Port GIG w/ 4xRJ45 & 2xSFP
- QuickTreX 10 Port GIG w/ 8xRJ45 & 2xSFP
- 4 Port Gigabit POE+ w/ 2 SFP Ports
- 4x10/100M TX PSE and 1x1000M SC MM
- 4x10/100M TX PSE + 1x10/100M
- 5 x RJ45 10/100/100BaseTX
- 5 x RJ45 1000Bast w/ 4 x Gig 30W PSE
- 8 x RJ45 10/100/1000m w/ v Boost
- 8 Port Gigabit POE+ w/ 2 SFP Ports
- 8 x Gig TX 30W PSE + 2 x 1000M TX/SFP w/ v Boost
- 8" Long Aluminum DIN Rail
- Managed Industrial PoE Switches
- Industrial Power Supplies
- SFP / QSFP Modules
- back
- Multimode SFP Modules
- Singlemode SFP Modules
- back
- 1.25 GIG - 2km at 1310nm by QuickTreX
- 10 GIG - 10km at 1310nm by QuickTreX
- 1F/BiDi Kit 1.25 GIG - 20km by QuickTreX
- 1.25 GIG - 20km at 1310nm by Unicom
- 1.25 GIG - 40km at 1310nm by Unicom
- 1.25 GIG - 80km at 1310nm by Unicom
- 1.25 GIG - 100km at 1310nm by Unicom
- 1.25 GIG - 120km at 1310nm by Unicom
- 1.25 GIG - 160km at 1310nm by Unicom
- 1.25 GIG - 180km at 1310nm by Unicom
- 10 GIG - 10km at 1310nm by Unicom
- 10 GIG - 40km at 1550nm by Unicom
- 10 GIG - 80km at 1550nm by Unicom
- 10 GIG - 100km at 1550nm by Unicom
- 10 GIG - 10km at 1310nm Cisco Compatible
- 1.25 GIG - 10km at 1310nm by Signamax
- Industrial SFP Modules
- back
- MM 1.25 GIG - 500 m / 850nm by QuickTreX
- SM 1.25 GIG - 20 km / 1310nm by QuickTreX
- MM 10 GIG - 300m / 850nm by QuickTreX
- SM 10 GIG - 10 km / 1310nm by QuickTreX
- MM GIG - 550m / 850nm by Signamax
- MM GIG - 2km / 1310nm by Signamax
- SM GIG - 10km / 1310nm by Signamax
- SM GIG - 40km / 1310nm by Signamax
- SM GIG - 40km / 1550nm by Signamax
- SM GIG - 80km / 1550nm by Signamax
- SM GIG - 110km / 1550nm by Signamax
- SM BiDI GIG - 10km 1310TX/1550RX
- SM BiDI GIG - 10km 1550TX/1310RX
- QSFP Modules
- back
- MM 40 GIG - 100m at 850nm
- SM 40 GIG - 10km at 1310nm
- SM 40 GIG - 40km at 1310nm
- MM 100 GIG - 12F MTP/MPO - 100m at 850nm
- SM 100GIG - DXLC - 2km at 1310nm
- SM 100GIG - DXLC - 40km at 1310nm
- SM 100GIG - DXLC - 80km at 1310nm
- MM 200 GIG - 12F MTP/MPO - 100m at 850nm
- MM 400 GIG - 12F MTP/MPO - 100m at 850nm
- SM 400GIG - DXLC - 2km at 1310nm
- Media Converters
- Network Racks and Cabinets
- back
- Free Standing Racks
- Open Frame Wall Rack
- back
- QuickTreX 16U (19"W x 18"D)
- Kendall Howard 8U (Adjustable W x 18"D)
- Kendall Howard 12U (Adjustable W x 18"D)
- Kendall Howard 12U Swing-Out
- Kendall Howard 18U Swing-Out
- Kendall Howard 12U Side Load
- Kendall Howard 12U (19"W x 12"D)
- Kendall Howard 16U (19"W x 12"D)
- Kendall Howard 12U (19"W x 18"D)
- Kendall Howard 16U (19"W x 18"D)
- Kendall Howard 2U Vertical w/ Tapped Rails
- Kendall Howard 4U Vertical w/ Tapped Rails
- Kendall Howard 2U Vertical
- Kendall Howard 4U Vertical
- Wall Mount Network Cabinets
- back
- QuickTreX 4U Swing-Out Hinged
- QuickTreX 4U Fixed
- QuickTreX 6U Swing-Out Hinged
- QuickTreX 6U Fixed
- QuickTreX 9U Swing-Out Hinged
- QuickTreX 9U Fixed
- QuickTreX 12U Fixed
- 6U Wall Mount - Glass Door
- 6U Wall Mount - Solid Door
- 6U Wall Mount - Vented Door
- 6U Swing Out Wall Mount - Glass Door
- 6U Swing Out Wall Mount - Solid Door
- 6U Swing Out Wall Mount - Vented Door
- 9U Wall Mount - Glass Door
- 9U Wall Mount - Vented Door
- 9U Wall Mount - Solid Door
- Network Rack & Cabinet Shelves
- Hardware, Fans, and Accessories
- Rack Mount Cable Management Panels
- Wireless Access Points
- Cable Wraps, Straps, and Ties
- back
- Pre-Cut Hook & Loop Velcro Cable Ties
- back
- 6" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 25 pcs
- 6" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 100 pcs
- 6" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 1200 pcs
- 8" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 25 pcs
- 8" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 100 pcs
- 8" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 900 pcs
- 12" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 25 pcs
- 12" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 100 pcs
- 12" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 600 pcs
- 18" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 25 pcs
- 18" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 100 pcs
- 18" x 1/2" Velcro Cable Ties - 400 pcs
- Bulk Roll Velcro Cable Strap
- Wall Mount Velcro Cable Straps
- Fire Retardant Hook & Loop Cable Ties
- back
- 8" x 1/2" Velcro Hook & Loop Ties - 10 pcs
- 8" x 1/2" Velcro Hook & Loop Ties - 100 pcs
- 8" x 1/2" Velcro Ties - 900 pcs
- 12" x 1/2" Velcro Hook & Loop Ties - 100 pcs
- 12" x 1/2" Velcro Hook & Loop Ties - 600 pcs
- 18" x 1/2" Velcro Hook & Loop Ties - 10 pcs
- 18" x 1/2" Velcro Hook & Loop Ties - 400 pcs
- 75 Ft x 1/2" Roll Velcro Cable Wrap Strap
- Economy Velcro Cable Ties
- Cable Bundle Socks
- Clip-On Velcro Cable Carrier
- TV & LCD Screen Mounts
- back
- Wall Mount TV/LCD Screen Mounts
- back
- 13" - 27" Screen w/ 10.4" Arm
- 13" - 42" Screen w/ 10.7" Arm
- 10" - 42" Screen w/ 7.5" Arm
- 10" - 42" Screen w/ 2.9" Arm
- 13" - 42" Screen w/ 14.3" Arm
- 26" - 47" Screen w/ 22.8" Arm
- 32" - 70" Screen w/ 18.4" Arm
- 37" - 80" Screen w/ 18.4" Arm
- 32" - 55" Screen
- 37" - 70" Screen
- 37" - 80" Screen
- XL 60" - 100" Screen
- Slim Fixed 32" - 55" Screen
- Fixed 32" - 55" Screen
- Fixed 37" - 70" Screen
- Ceiling Mount TV/LCD Screen Mounts
- NPT Pipe TV Ceiling Mounts
- back
- 1.5" NPT Pipe Mount 32" - 55" Screen
- 1.5" NPT Pipe Mount 23" - 42" Screen
- 1.5" Double Sided NPT Mount 32"-55"
- 1.5" NPT Mount 37"-70"
- Flat Ceiling Plate for 1.5" NPT Pipe
- Angled Ceiling Plate for 1.5" NPT Pipe
- 1.5" NPT x 34.4 Long NPT Pipe
- Adjustable NPT Pipe 1.5"D x 8.66-14.57"L
- 1.5" NPT Pipe Coupler
Login
The Stages of an OSP Installation: From Planning to Testing
In the world of modern communication and data transmission, Outside Plant (OSP) installations play a crucial role in connecting businesses, homes, and communities.
From high-speed internet to telecommunications networks, OSP projects are the backbone of our connected world.
This blog will take you through the various stages of an OSP installation, from the initial planning and design phase to the installation of fiber and comprehensive testing.
Table of Contents
Stage 1: Design
Planning the Route of Your Network
The first and most critical stage of an OSP installation is designing the network's route. Here, you'll make several crucial decisions:
Aerial, Direct Burial, Underground, or Underwater?
Depending upon the route your cables need to travel, you may need one of, or a combination of, these OSP project types.
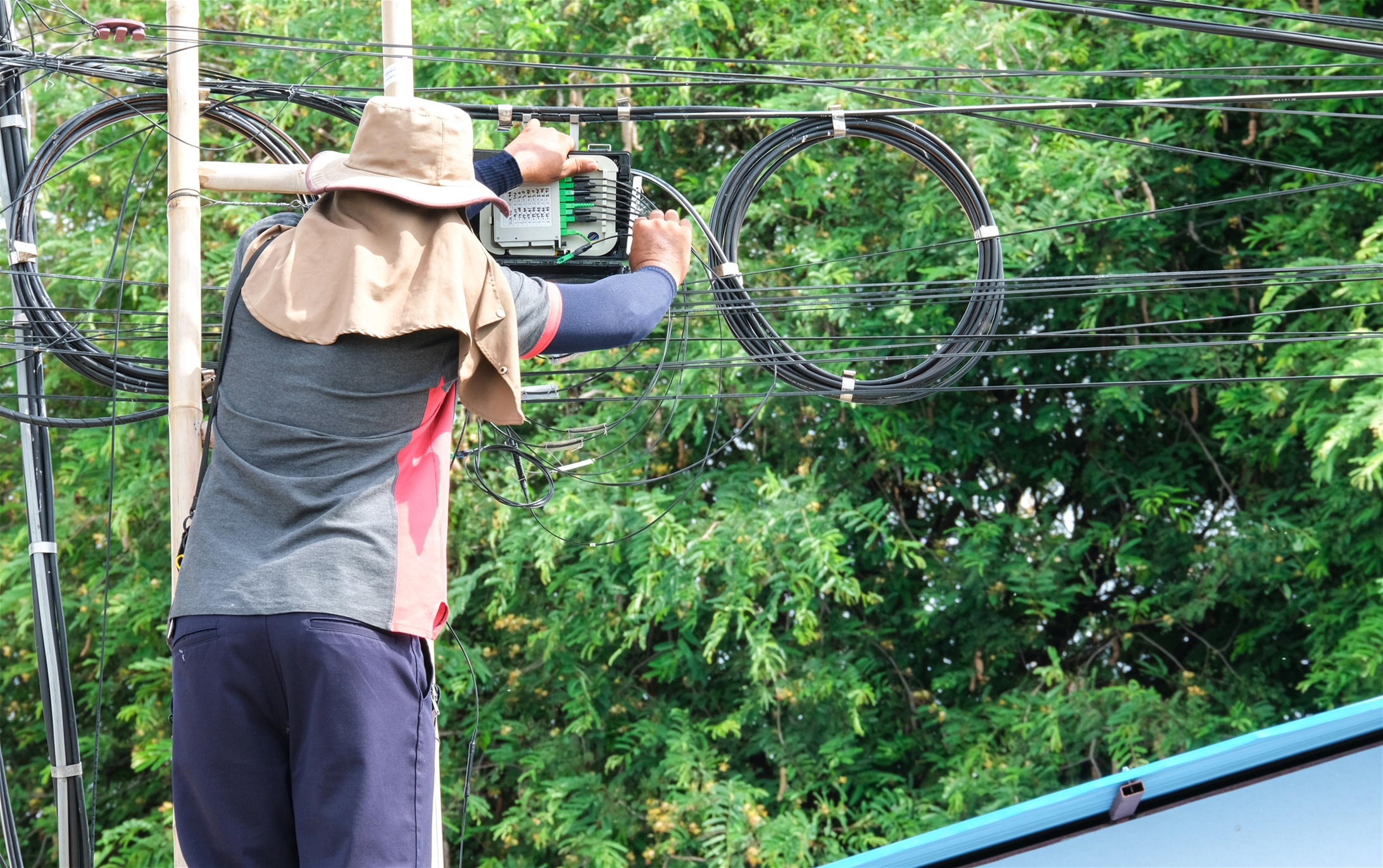

Aerial installations involve hanging cables on utility poles and are common in suburban and rural areas.
Direct burial involves burying cables directly underground, which is suitable for less populated areas.
Underground installations use conduits or trenches for cable placement, ideal for urban environments.
Underwater installations, though less common, are used for subsea cables.
In order to determine which method(s) you may need, you should always conduct a site visit.
Site Visits and Safety Measures
Conducting thorough site visits are very important in order to assess the terrain and local conditions you or your installation team will encounter. A site visit is often a requirement for contractors to even be able to bid on the project.
These site visits include walking or driving every foot of the route to determine what obstacles you may see.
The site visit will also uncover what areas your team will need to dig, if you are implementing direct burial or underground OSP projects. Implementing a safe digging practice and getting the right permits will help to avoid accidentally damaging any existing cable infrastructure.
If you are connecting your outdoor installation to an indoor premise, you’ll want to inspect every area of the building to understand what any hazards to watch out for, such as fire hazards.
Finally, you’ll need to obtain the necessary permits and permissions for digging and construction your installation team will conduct. Always call before you dig, not only to avoid damage, but also to avoid unknown high voltage electrical cables or high pressure gas lines.
Selecting the Right Equipment
Selecting the right type of fiber is crucial for your project, as singlemode and multimode fibers serve different purposes. While singlemode used to be the go-to choice for all OSP projects, advancements in technology have expanded the options. In fact, many OSP projects now incorporate both singlemode and multimode fibers.
For underground cabling installations, using a 4-inch conduit pipe is an excellent choice. This not only safeguards your cables but also ensures easy maintenance in the future.
To simplify cable installation and potential repairs, consider employing pulling tape, which can streamline both processes.
In cases of aerial cables, you may need to install supporting structures such as poles and towers if they're not already in place.
For underground installations, inner-duct manholes and vaults are essential components to consider.
Lastly, it's crucial to map out a dedicated storage space for excess cables and equipment, ensuring efficient management and future maintenance.
Stage 2: Installation of Fiber
The installation of fiber is a critical phase in the OSP project, where the well-planned design begins to take physical shape. This stage involves a series of tasks and steps to ensure that the fiber cables are correctly placed, protected, and secured.
Cable Installation
Preparation
Before installation begins, ensure that the cable reels and associated equipment are on-site and ready for use. Organize the cables and verify their lengths to match the design plan.
Cable Pulling
For aerial installations, cables are pulled through overhead support structures like utility poles and towers. For underground installations, they are laid in conduits or trenches. This process requires specialized equipment like cable pulling machines and tension monitors to ensure a smooth and controlled installation.
Conduit Placement
In underground installations, conduits are often used to house and protect the fiber cables. Careful attention must be paid to conduit placement to prevent bends or kinks that can affect signal quality.
Splicing
In situations where multiple cable segments need to be joined, splicing is performed. Fiber splicing can be done using fusion splicing or mechanical splicing, depending on the project's requirements and specifications.
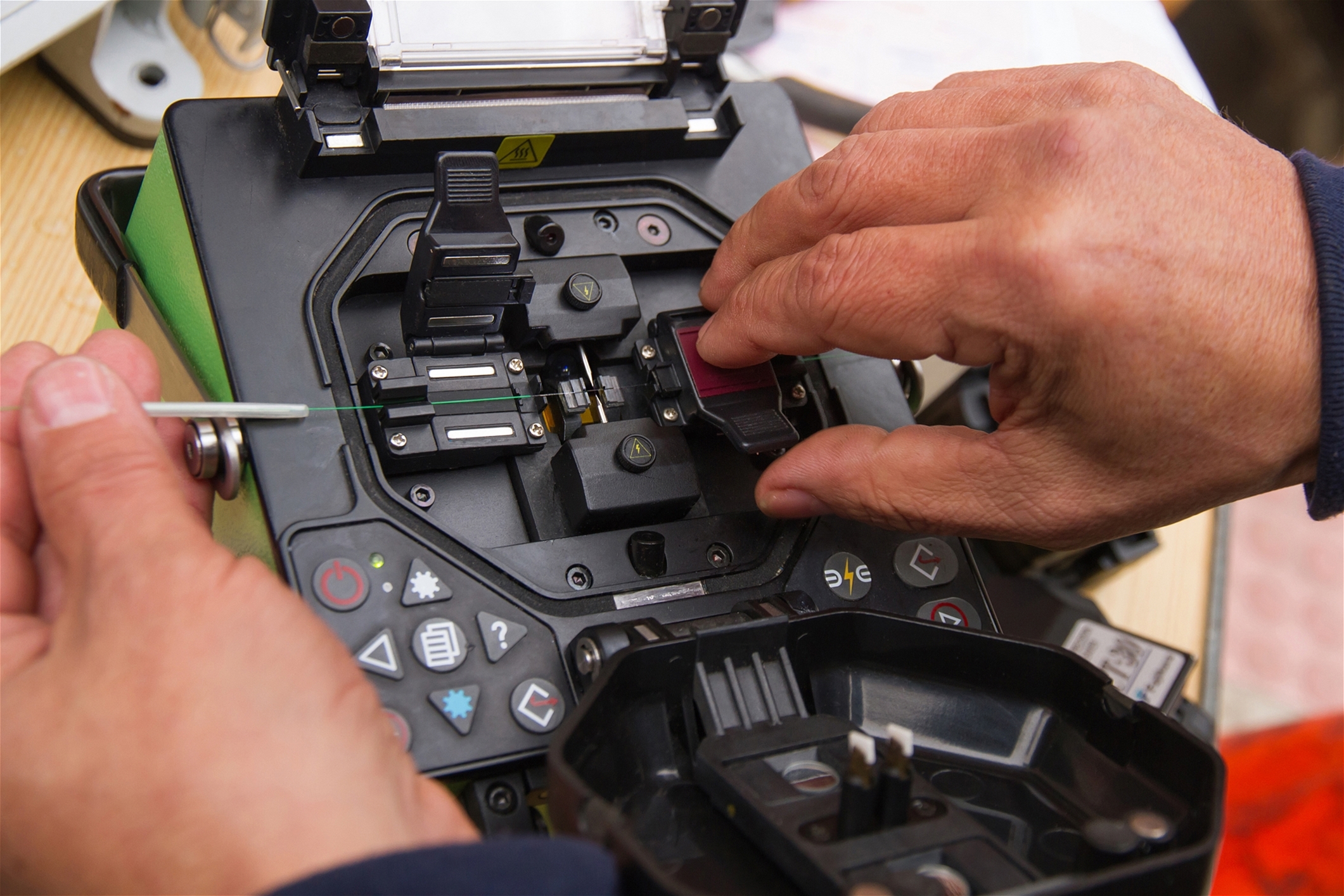

Sealing and Encapsulation
For underground or underwater installations, it's essential to ensure that the fiber cables are sealed and encapsulated properly to protect them from moisture, dirt, and environmental factors. This helps maintain the integrity of the network.
Cable Tension
Maintaining the proper tension while pulling the cables is crucial to prevent damage. Excessive tension can cause fiber breaks or signal loss, while insufficient tension can lead to slack loops.
Installation in Vaults and Inner-Duct Manholes: In underground installations, inner-duct manholes and vaults are used to provide access points for maintenance and repairs. Careful installation and labeling of cables within these structures are vital for efficient future network management.
Safety and Quality Control
During the installation of fiber, it's paramount to adhere to safety guidelines and maintain quality control.
Implement strict safety measures to protect workers, pedestrians, and the environment.
This includes using appropriate personal protective equipment, cordoning off work areas, and preventing accidents or damage to existing infrastructure.
For quality control, you should inspect the cables and splices to ensure they meet the specified standards and design criteria. Any deviations or discrepancies should be addressed promptly to maintain network integrity.
Cable Management
Proper cable management is essential for OSP installations.
Ensure that the cables are routed along the planned paths and secured to supporting structures such as poles, towers, or conduit clamps.
Create service loops in appropriate locations to allow for future expansion or repairs without excessive cable tension or the need for additional splicing.
Each cable should be labeled accurately to aid in troubleshooting and maintenance. Clear and consistent labeling is essential for efficient network management.
Document the installation process, including cable types, lengths, splice locations, and any deviations from the initial design. This documentation is invaluable for future reference.
By paying meticulous attention to the installation phase, you can ensure that the fiber network is installed correctly, and the foundation for a robust OSP system is established.
Proper installation sets the stage for the next crucial phase: testing the network to confirm its reliability and performance.
Stage 3: Testing
Developing a Test Plan
After the fiber is installed, rigorous testing is necessary to guarantee the network's performance and reliability.
Develop a comprehensive test plan that outlines the testing process, criteria, and goals.
Tools Needed for Testing

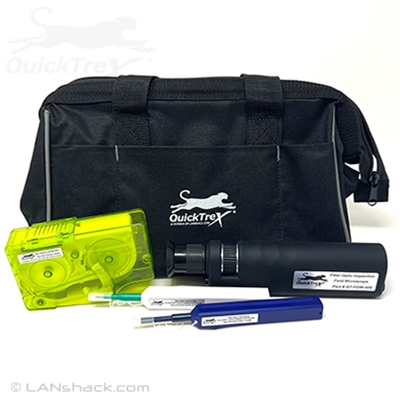
Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (OTDR)
Used to measure signal loss and identify faults in the fiber.
Troubleshooting
Identify and address any issues found during testing, such as signal loss or faulty splices. Troubleshooting is essential for ensuring a high-quality OSP network.
Documentation
Keep thorough records of the test results and troubleshooting steps. Proper documentation is essential for future reference and network maintenance.
Planning for Future Repairs
It's vital to plan for the future by considering potential repairs and upgrades. This may involve ensuring accessibility to splice points, keeping detailed records, and having a maintenance plan in place.
Conclusion
An OSP installation is a complex and multi-stage process that requires meticulous planning, careful execution, and thorough testing. By following these stages and guidelines, you can ensure a reliable and efficient OSP network that connects people and communities to the digital world. From the initial design and equipment selection to the installation of fiber and comprehensive testing, each stage plays a critical role in the success of the project. With the right preparation and attention to detail, you can build a robust OSP network that stands the test of time.
 888-568-1230
888-568-1230